In the second quarter of 2024, several new and evolving cyber threats were detected. Cybercriminals are finding smarter ways to attack, making it harder for security systems to protect users. The HP Wolf Security Threat Insights Report – September 2024 highlights the most important threats that were spotted during this time.
These include malware that uses artificial intelligence (AI), an increase in browser hijackers, and the misuse of image files to hide dangerous code.
Here’s a simple table that summarizes the key points and cybersecurity threats from the HP Wolf Security Threat Insights Report – September 2024 for an easier overview:
| Threat Type | Description | Key Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Powered Malware | Cybercriminals use Generative AI (GenAI) to create and spread malicious software. | GenAI was likely used to write AsyncRAT, a malware that allows attackers to control infected systems. |
| ChromeLoader Malware | Browser hijacker that redirects users to attacker-controlled websites for ad fraud. | Disguises as useful software (e.g., PDF tools). Uses real security certificates to avoid detection. |
| SVG File Exploits | Embedding malicious JavaScript code into SVG images, which are often used in web design. | When opened in a browser, the SVG file downloads other malware, including Venom RAT and Remcos. |
| Email-Based Attacks | Email remains the primary attack vector, delivering 61% of malware in Q2 2024. | Many phishing emails and dangerous attachments bypassed security filters. |
| Web Downloads | Fake software downloads trick users into installing malware like ChromeLoader. | Common disguises include tools like PDF converters and recipe guides. |
AI-Powered Malware
One of the most concerning developments is how hackers are now using generative AI (GenAI) to create malware. GenAI has been used to trick people with convincing emails, but now it’s being used to write malicious code. This means attackers don’t need to be experts to create dangerous programs.
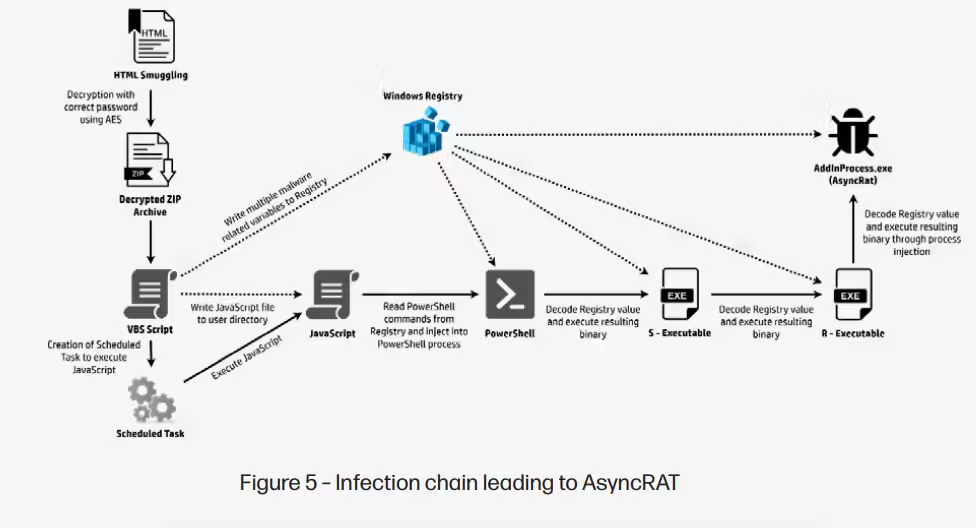
For example, the report found that AI was likely used to write the code for AsyncRAT, a remote access trojan (RAT). This is a type of malware that lets attackers take control of a computer from anywhere. The scripts used in this attack had clear signs of being written by AI, such as well-organized code and detailed comments. This shows that AI is helping hackers work faster and more effectively.
ChromeLoader: A Sneaky Browser Hijacker
Another major cybersecurity threats is ChromeLoader, a malware that takes over web browsers. ChromeLoader tricks users by pretending to be useful software, like PDF converters or other free tools. Once installed, it changes the way the browser works, redirecting the victim to dangerous websites. These websites are controlled by attackers and are used to make money through ad fraud.
What makes ChromeLoader harder to detect is its use of real security certificates. These certificates make it look like the malware is safe and trustworthy, allowing it to bypass many security checks. This makes it even more dangerous and difficult to remove.
Hidden Threats in SVG Image Files
Cybercriminals are also using new techniques to infect computers. One of the more creative attacks involves using Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) files. SVG files are commonly used for images on websites. Hackers are hiding JavaScript code inside these image files, which can run when the image is opened in a browser.
When a user opens the infected SVG file, it starts a chain reaction. The file tricks the computer into downloading other dangerous files, leading to infections by various malware types, including Venom RAT and Remcos. This type of cybersecurity threats is unusual and highlights how attackers are always looking for new ways to avoid detection.
Email: Still the Most Common Attack Method
Despite the new tactics, email remains the top way attackers spread malware. According to the report, 61% of threats were delivered through email, including phishing scams and dangerous attachments. Many of these threats were able to sneak past security filters, making email one of the riskiest activities for businesses and individuals.
Conclusion
The threats detected in Q2 2024 show how fast cybercriminals are adapting. They are using AI to make malware more powerful, finding ways to trick people through fake software like ChromeLoader, and hiding dangerous code in places we wouldn’t expect, like SVG files.
It’s important for businesses and users to stay alert and update their security measures regularly to keep up with these evolving cybersecurity threats.
